1. What Is Plant Tissue Culture?
Plant tissue culture refers to a collection of in vitro (in glass/lab) techniques used to grow plant cells, tissues, or organs in a controlled, sterile environment. These methods enable scientists, researchers, and growers to:
-
Clone elite plant varieties
-
Preserve endangered species
-
Modify plant genetics
-
Produce disease-free planting material
-
Extract valuable secondary metabolites
Originally developed for research, plant tissue culture is now a foundational tool in agriculture, horticulture, forestry, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
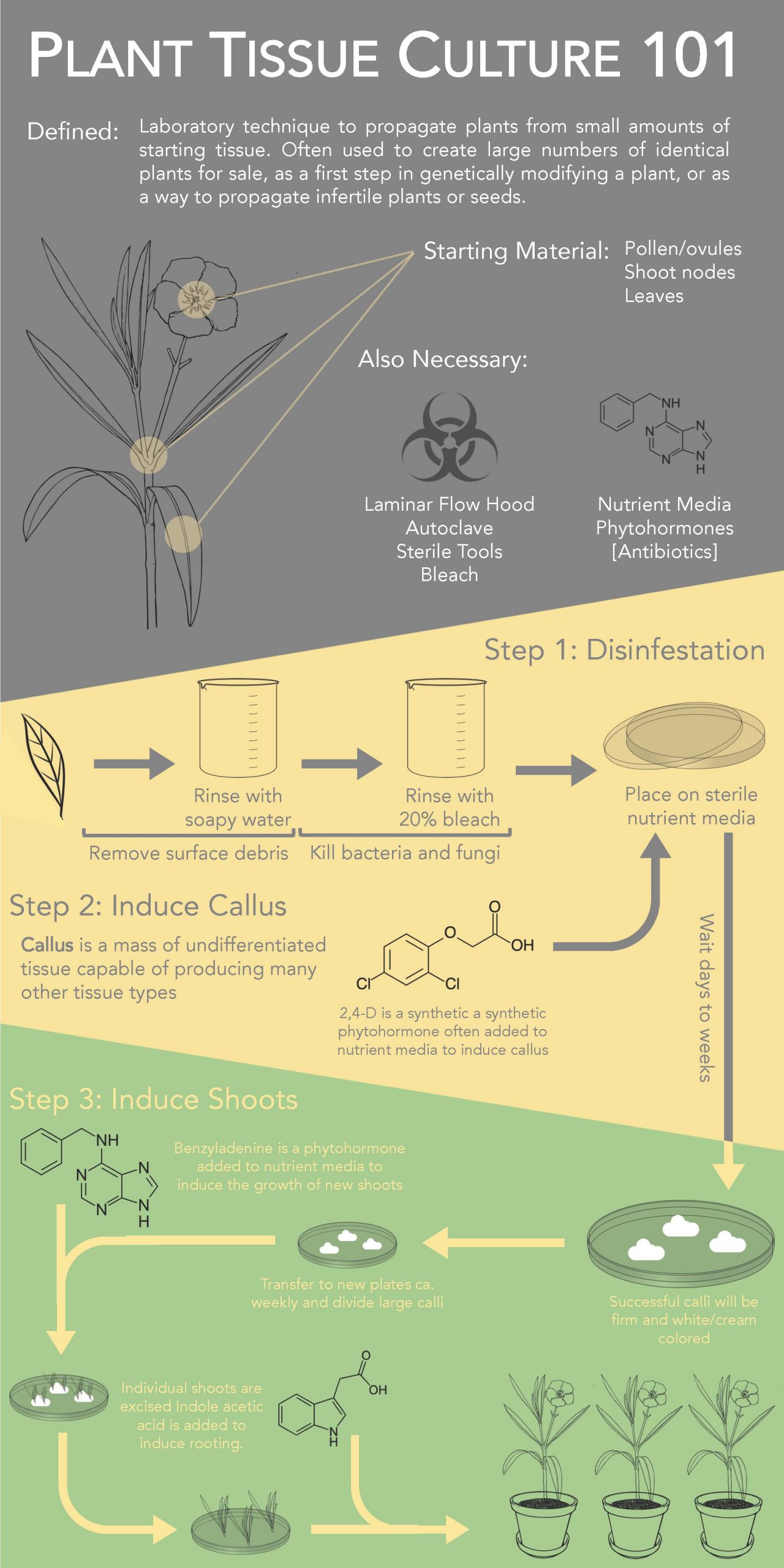
2. How Plant Tissue Culture Works: Step-by-Step Overview
The process typically involves the following stages:
-
Explant Selection:
A small piece of plant tissue (leaf, root, stem, meristem, etc.) is selected from a healthy donor plant. -
Surface Sterilization:
The explant is sterilized using chemicals (e.g., sodium hypochlorite or ethanol) to eliminate microbial contamination. -
Culture Initiation:
The sterile tissue is transferred onto a nutrient-rich culture medium, usually agar-based, under aseptic conditions. -
Cell Division and Development:
Cells divide and either form:-
Callus (undifferentiated mass of cells), or
-
Begin organogenesis (shoot and root formation).
-
-
Plantlet Multiplication:
Shoots and roots continue growing under controlled light, temperature, and humidity, forming complete plantlets. -
Hardening and Acclimatization:
The plantlets are gradually transferred to non-sterile environments (greenhouses or outdoor conditions), allowing them to develop tolerance to natural stressors.
3. Major Types of Plant Tissue Culture
| Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Callus Culture | Growth of undifferentiated cells induced by auxins | Genetic modification, metabolite production |
| Organ Culture | Growth of specific organs (roots, shoots) | Commercial micropropagation |
| Cell Suspension Culture | Cultivation of plant cells in liquid media | Biopharmaceuticals, scaling metabolite extraction |
| Protoplast Culture | Culture of cells with cell walls removed | Somatic hybridization, genetic fusion, transformation |
Each technique is adapted to the species, purpose, and production goals.
4. Why Is Plant Tissue Culture Important?
Tissue culture offers several key advantages:
-
Mass Propagation: Rapid production of thousands or millions of genetically identical plants.
-
Disease-Free Plants: Explant from meristem regions can eliminate viruses and pathogens.
-
Conservation: Ex situ preservation of endangered or rare plants (cryopreservation, slow growth storage).
-
Genetic Engineering: Used as a gateway for CRISPR and transgenic integration.
-
Medicinal Production: Controlled growth of plants like Artemisia, Taxus, and Withania for pharmaceutical extraction.
📌 FAO Guide to Plant Tissue Culture Applications
5. Real-World Applications of Tissue Culture
| Sector | Application |
|---|---|
| Agriculture & Horticulture | Banana, sugarcane, potato, orchid micropropagation |
| Forestry | Clonal propagation of elite trees (e.g., teak, eucalyptus) |
| Pharmaceuticals | Large-scale cultivation of plants for antimalarial (Artemisia), anticancer (Taxus), and adaptogenic (Withania) compounds |
| Biotechnology | Drought- and pest-resistant crops, biofortified food (e.g., Golden Rice) |
| Space Research | NASA and other space agencies test tissue culture for closed-loop plant growth in extraterrestrial habitats |
6. Future Directions in Plant Tissue Culture
Modern labs are incorporating:
-
CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to create designer crops
-
Automated systems for media dispensing and culture handling
-
Organic media using coconut water, banana extract, or seaweed
-
Biofactories producing flavors, fragrances, and pharmaceuticals
-
Climate-resilient agriculture via lab propagation of stress-tolerant species
📌 Emerging Trends in Tissue Culture
Conclusion
Plant tissue culture is a revolutionary tool at the intersection of plant biology, biotechnology, and commercial agriculture. From cloning superior cultivars to preserving biodiversity and enabling pharmaceutical breakthroughs, it plays a vital role in solving real-world challenges.
As you move through this course, you’ll build both a technical and practical understanding of how these techniques can be used across many industries—and how you can be a part of their future.